Municipal Administration of Traditional Chinese Medicine, Municipal Hospital Management Center, District Health and Health Committees, and relevant medical and health institutions:
In order to implement the Three-year Action Plan for Strengthening the Construction of Public Health Emergency Management System in Beijing (2020-2022) and strengthen the construction of public health system in our city, we hereby print and distribute the Beijing Training Plan for Medical Prevention Integration (2020 -2022) to you, please follow it. If you have any questions, please feedback to our Committee in time.
Beijing Municipal Health and Wellness Committee
December 1, 2020
(Contact person and contact information: Jingjing Shi, 83970736; Bai Bing, 83970737)
Beijing Medical and Prevention Integration Training Program (2020 -2022)
In order to implement the spirit of the opinions of the municipal party committee and municipal government on strengthening the construction of public health emergency management system and the requirements of the action plan, improve the ability of health professionals in disease prevention and control institutions, pre-hospital medical emergency institutions and secondary and tertiary medical institutions to deal with public health emergencies, and strengthen the integration of medical care and public health, this plan is formulated in light of the actual situation of this Municipality.
I. Guiding ideology
Guided by the integration of medical care and prevention, around the cross-training needs, improve the training system with the core of competence in dealing with public health emergencies. By carrying out standardized training to fill shortcomings, plug loopholes and strong and weak items, we will build a team of high-quality, skilled and capable medical and preventive compound backbone doctors, and further improve the emergency support ability and level of public health emergencies in the city.
Second, the training objectives
Through the planned and organized training on the integration of medical care and prevention, by 2022, the number of health professionals and technicians who have cross-trained among disease prevention and control institutions, pre-hospital medical emergency institutions and secondary and tertiary medical institutions in the city will reach more than 600, and a number of training bases and training materials combining public health with clinical medical care will be built.
Third, the training target
(a) two or three medical institutions to be promoted to vice high titles of internal medicine (including internal medicine, pediatrics, emergency department, general practice, infectious diseases) physicians.
(two) the emergency center intends to be promoted to the vice high title of clinician.
(three) the Center for Disease Control and Prevention intends to be promoted to a public health physician with the title of associate senior.
(4) Other doctors who voluntarily participate in the training.
Fourth, the training content
Clinicians in secondary and tertiary medical institutions mainly strengthen public health emergency ability, pre-hospital medical emergency ability and infectious disease diagnosis and treatment ability. Clinicians in emergency centers and public health doctors in centers for disease control and prevention mainly focus on strengthening the ability of clinical diagnosis and treatment, prevention and control of nosocomial infection and diagnosis and treatment of infectious diseases.
(A) public health emergency response capacity
Laws and regulations on the prevention and control of infectious diseases, key points and prevention and control schemes for emerging and sudden infectious diseases, health emergency response strategies for public health emergencies, skills in dealing with infectious diseases such as protection, isolation, transshipment and disinfection, epidemiological investigation techniques and other public health emergency knowledge and technologies. For details, please refer to the Detailed Rules for Public Health Emergency Response Training (Annex 1).
(B) clinical diagnosis and treatment and hospital infection prevention and control capabilities
For the key points, the diagnosis and treatment plan and early detection ability of new and sudden infectious diseases, the principle of treatment for critically ill patients, and the system and measures for prevention and control of nosocomial infection, please refer to the Training Rules for Clinical Diagnosis and Treatment and Prevention and Control of Hospital Infection (Annex 2) for specific requirements.
(3) Pre-hospital medical first aid ability
Pre-hospital medical first aid laws and regulations, basic first aid skills, on-site disposal principles, emergency response capabilities, etc. For specific requirements, please refer to the Detailed Rules for Pre-hospital Medical First Aid Training (Annex 3).
V. Training Form and Time
The integration training of medical care and prevention includes three training modules: course study, practical training and on-the-job training, and the cumulative training time is 6 months.
(A) course learning
Various laws and regulations, documents and work plans, basic theoretical knowledge, etc., take classroom teaching or internet plus teaching to carry out training.
(B) Practical training
The contents with high practical requirements, such as public health incident investigation and on-site disposal, personal protection and basic skills of clinical diagnosis and treatment, are carried out by interactive teaching methods combining scenario or simulation teaching, drills and skill assessment.
(3) Post exercise
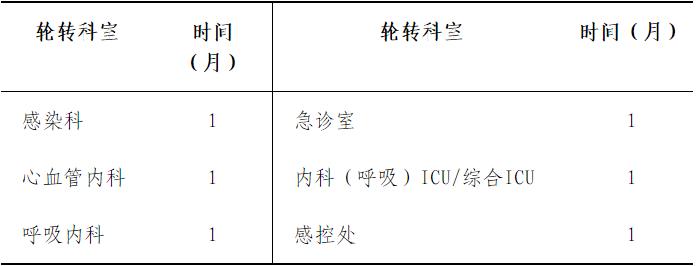
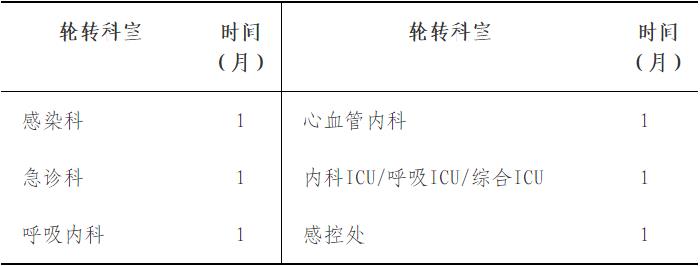
According to the training needs and actual work arrangements, the trainees can go to the recognized training bases (including general hospitals, infectious disease hospitals, emergency centers and centers for disease control and prevention, etc.) for short-term training and on-the-job training, and the accumulated training period is not less than half a year before being promoted to the title of deputy senior high school. Among them, clinicians in secondary and tertiary medical institutions go to infectious disease hospitals for one month, emergency centers for not less than three months, and CDC for not less than two months (including course study and practical training); Doctors in emergency center and CDC should go to infectious disease hospital for further study for one month, and general hospital for further study for not less than five months (including course study and practical training).
Sixth, the training base
According to the training contents, the training bases for medical and prevention integration are the municipal and 16 district centers for disease control and prevention, Beijing Emergency Center, beijing ditan hospital affiliated to Capital Medical University, Beijing You ‘an Hospital affiliated to Capital Medical University, and the hospitals where the national standardized training base for internal medicine residents is located. For the list, see the Directory of Beijing Medical and Prevention Integration Training Bases (Annex 4).
Seven, training registration, assessment and certification
(1) Registration
Those who apply for training should fill in the Registration Form of Beijing Medical Prevention Integration Training (Annex 5) and apply to the training department of their unit. After the unit summarizes, they should fill in the Summary Form of Beijing Medical Prevention Integration Training (Annex 6) and put forward training needs to the training base, and the training base will arrange training according to the needs. The specific registration schedule will be announced separately.
(2) Examination and certification
The training base will assess the personnel who have completed the training. After passing the assessment, the training base will record it on the Training Certificate of Beijing Medical Prevention Integration (Annex 7) and affix the official seal of the unit. "Beijing Medical Prevention Integration Training Certificate" is an important basis for my promotion to deputy senior title.
VIII. Safeguard measures
(A) to strengthen organizational management
The Beijing Municipal Commission of Health and Wellness co-ordinates and manages the training of the integration of medical treatment and prevention in the whole city, sets up an expert committee on the integration of medical treatment and prevention, formulates training plans and detailed rules, makes full use of the high-quality resources of universities, public health institutions and medical institutions in Beijing, compiles training materials, compiles training courseware, organizes training, and supervises and assesses the training work in the whole city. The district health and wellness committees are responsible for mobilizing and deploying the cross-training of medical and prevention integration in medical and health institutions under their jurisdiction, organizing qualified trainees of relevant medical and health institutions to participate in the training, strengthening the construction of regional disease prevention and control centers and emergency stations, and assisting in the coordination and supervision of training. The training base is responsible for implementing the training plan according to the training requirements and registration arrangements, strictly conducting graduation examination, improving the safeguard measures, and effectively ensuring the training quality. The secondary and tertiary medical and health institutions, emergency centers (stations) and CDC shall, according to the training requirements, reasonably arrange relevant professionals to participate in the training, and provide necessary guarantee conditions for the trainees.
(B) improve the incentive measures
Medical and preventive integration training is included in the compulsory project management of continuing medical education at the municipal level, and continuing education credits can be obtained according to relevant regulations after completing the training. Physicians in internal medicine (internal medicine, pediatrics, emergency department, general practice, infectious diseases department) and emergency centers (stations) and centers for disease control and prevention at all levels in the second and third-level medical institutions in this city shall complete the training of medical prevention integration for not less than half a year before being promoted to the title of deputy high school, and the training time shall be included in the service time of medical personnel to rural grassroots or community health service institutions. From 2021 onwards, those who have completed the training of integration of medical care and prevention will be recommended for promotion first, and from 2023 onwards, it will be one of the necessary conditions for promotion. Other physicians who voluntarily participate in and complete the training of integration of medical care and prevention shall apply the provisions of this scheme and be recommended first before being promoted to the title of associate senior high school.
(3) Guarantee the investment of funds
The training funds for the integration of medical care and prevention are invested by the government, units and society. The municipal finance arranges special funds to ensure the compilation of teaching materials, courseware recording, practical teaching, supervision and assessment, etc. The training base provides necessary learning and living conditions for the implementation of training. The unit where the trainees work provides them with convenient conditions and guarantees their treatment during the training period. Encourage social funds to support the training of medical and prevention integration.
Attachment: 1. Detailed Rules for Training Public Health Emergency Response Capability
2. Training rules for clinical diagnosis and treatment and hospital infection prevention and control ability
3. Pre-hospital medical emergency ability training rules
4. List of Beijing Medical Prevention Integration Training Bases
5. Beijing Medical Prevention Integration Training Registration Form
6. Beijing Medical Prevention Integration Training Summary Table
7. Beijing Medical Prevention Integration Training Certificate
Annex 1
Detailed Rules for Training Public Health Emergency Response Ability
First, the basic knowledge of public health emergency management
(1) Training time: 6 hours of theoretical teaching and 6 hours of practical training.
(2) Training place: municipal and district disease prevention and control institutions.
(3) Training contents:
1. Be familiar with the contents of the Law on the Prevention and Control of Infectious Diseases in People’s Republic of China (PRC), and master the relevant rights, obligations and work requirements of employees in medical and health institutions.
2. Learn the Regulations of Beijing Municipality on the Administration of Public Health Emergencies, and understand the definition standards, disposal procedures and management requirements of major public health emergencies.
Second, infectious disease monitoring and management
(1) Training time: 12 hours of theoretical teaching and 1-2 weeks of practical training.
(2) Training place: municipal and district disease prevention and control institutions.
(3) Training contents:
1. Familiar with the legal infectious diseases and classification, understand the information reporting and management norms of infectious diseases and public health emergencies, and master the management process and basic requirements of infectious disease epidemic monitoring report.
2. Be familiar with the operation and operation of the network direct reporting system of infectious diseases, and master the definition and standard of routine reporting information.
3. Master the principles, methods and main evaluation indexes of quality verification of infectious disease epidemic reports in medical institutions, and write quality evaluation reports.
Iii. Epidemiological investigation and on-site disposal
(1) Training time: 24 hours of theoretical teaching, 6 hours of practical training and 4-6 weeks of on-the-job training.
(2) Training place: municipal and district disease prevention and control institutions.
(3) Training contents:
1. Understand the concept of epidemic situation of infectious diseases, general principles and procedures for investigation and handling; To master the purpose, significance, basic principles and contents of epidemiological investigation.
2. Understand the definition, general investigation and handling principles and procedures of outbreaks, major epidemics and public health emergencies.
3. Understand the basic knowledge of diseases requiring case investigation and the main epidemic control measures.
4. Understand the judgment criteria, investigation and handling principles and handling procedures of clustering cases and outbreaks of key infectious diseases.
5. Master the principles, objectives, significance, technical standards and contents of the main control measures for infectious diseases. Including the judgment of close contacts and cases, isolation management, active search method, disinfection of environment and articles, protection of susceptible people, etc.
6. Master the collection and transportation methods and norms of biological samples and external environmental samples in the epidemic situation of infectious diseases.
7. Master the epidemiological investigation skills and the specifications and requirements for writing investigation reports.
Annex 2
Training rules for clinical diagnosis and treatment and hospital infection prevention and control ability
I. Training Time
Post exercise for 6 months, including 1 month in infectious disease hospital and 5 months in general hospital.
Second, the training place
Infectious disease specialist hospital (beijing ditan hospital affiliated to Capital Medical University and Beijing You ‘an Hospital affiliated to Capital Medical University) and general hospital (Beijing standardized training base for resident doctors).
Third, the training content
(1) Personnel of public health institutions
Participate in the daily work and teaching activities of the Sense Control Department by participating in patient management, clinical rounds and various teaching activities. Learn professional theoretical knowledge and skills related to the training requirements of the ability of combining medical treatment with prevention.
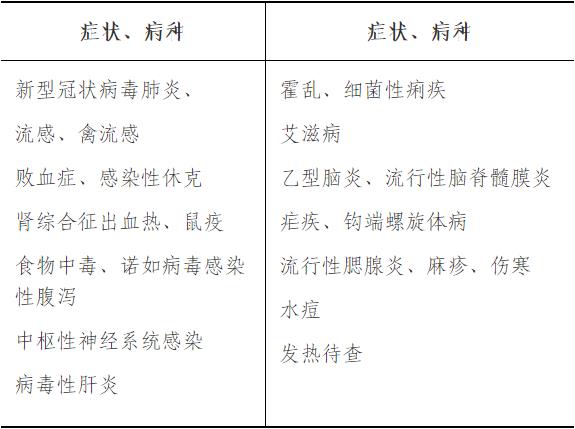
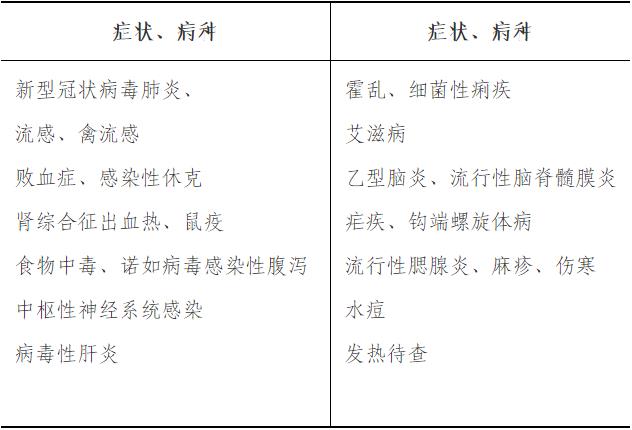
Infectious Disease
1. Rotation purpose
Master:
(1) Disinfection, isolation and protection measures for infectious diseases;
(2) novel coronavirus’s knowledge of etiology, epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic basis, differential diagnosis and treatment principles;
(3) Etiological knowledge, epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic basis, differential diagnosis and treatment principles of influenza and avian influenza;
(4) legal infectious disease reporting and handling procedures.
Familiar with:
(1) Clinical epidemiology and prevention of nosocomial infection;
(2) Etiological knowledge, epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic basis, differential diagnosis and treatment principles of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome and plague;
(3) Principles of diagnosis, differential diagnosis and treatment of intestinal infectious diseases such as typhoid fever, bacillary dysentery, amoebiasis and bacterial food poisoning; Etiological knowledge, epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic basis, differential diagnosis and treatment principles of norovirus-infected diarrhea;
(4) Etiological knowledge, epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic basis, differential diagnosis and treatment of hepatitis A, B, C and E; Antiviral treatment of chronic hepatitis B and hepatitis C;
(5) Etiological knowledge, natural history, clinical manifestations, primary screening and confirmation, and antiviral treatment principles of human acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS);
Understand:
(1) Etiological knowledge, epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic basis, differential diagnosis and treatment of new Bunia virus infection (fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome);
(2) Etiological knowledge, epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic basis, differential diagnosis and treatment of yellow fever, dengue fever, Zika and malaria;
(3) Etiological knowledge, epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic basis, differential diagnosis and treatment of anthrax and brucellosis; Etiological knowledge, epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic basis, differential diagnosis and treatment of Ebola hemorrhagic fever
(4) Diagnosis and treatment of parasitic diseases;
(5) Pathogenesis and anti-shock treatment of sepsis and septic shock;
(6) Clinical application of antibacterial drugs.
2. Basic requirements
(1) learning symptoms, disease requirements:
No less than 12 inpatients are required to participate in the management.
(2) Basic skill requirements:
Procedures for disinfection and isolation; Graded protection requirements. Carry out intensive practice rotation in fever clinic
3. Higher requirements
On the basis of basic requirements, you should also learn the following diseases and skills.
(1) learning diseases:
Diagnostic thinking of infectious mononucleosis, toxoplasmosis, rabies and fever of unknown origin.
(2) Clinical knowledge and skills requirements:
Lumbar puncture operation
Cardiovascular Department (1 month)
1. Rotation purpose
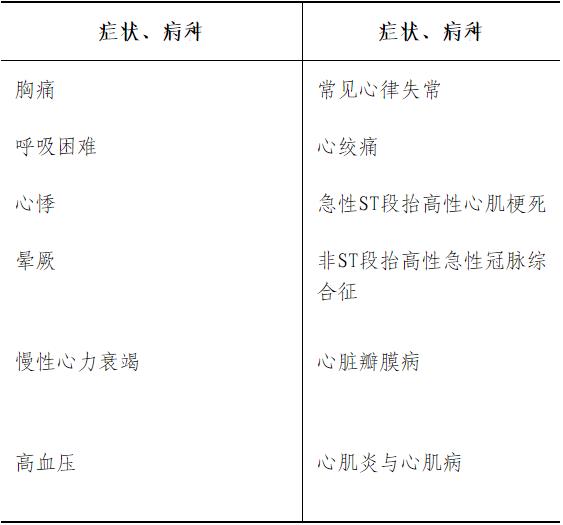
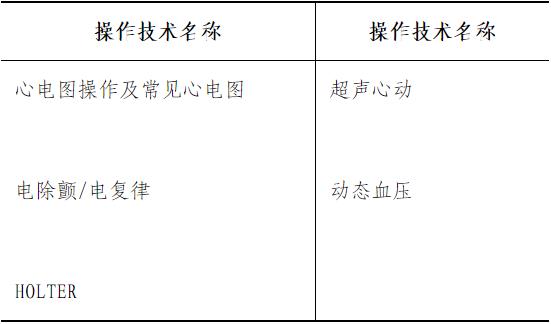
Familiar with: the diagnosis and differential diagnosis of common symptoms of cardiovascular system (including chest pain, dyspnea, palpitation and syncope); Pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, differential diagnosis and treatment of common cardiovascular diseases; Diagnosis and treatment of acute and severe cardiovascular diseases; Application of commonly used drugs for cardiovascular diseases; Common typical ECG diagnosis; Electrical defibrillation technology.
Understanding: Basic knowledge of cardiac electrophysiology, coronary angiography, PCI therapy, cardiac pacing, ambulatory electrocardiogram, ambulatory blood pressure and echocardiography.
2. Basic requirements
(1) trainee symptoms, disease requirements
It is required to participate in the management of at least 10 inpatients.
(2) Basic inspection and operation trainee
Respiratory medicine (1 month)
1. Rotation purpose
Familiar with: the diagnosis and differential diagnosis of cough, expectoration, hemoptysis and dyspnea; Epidemiological characteristics, diagnosis and treatment principles of upper respiratory tract infection and influenza; Diagnosis, differential diagnosis and treatment of pneumonia; Clinical manifestations, diagnosis and treatment principles of bronchial asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; Clinical manifestations, principles of diagnosis and treatment of lung cancer; Concept, classification, clinical manifestations and principles of diagnosis and treatment of respiratory failure.
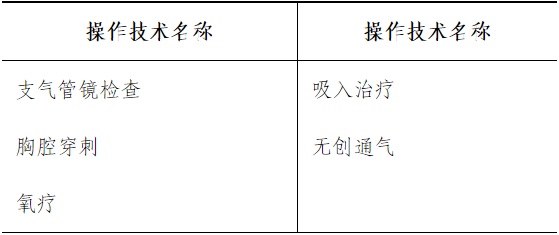
Understand: the pathogenic examination method of pneumonia, the operation method and clinical significance of bronchoscope and medical thoracoscope, the inhalation treatment of respiratory drugs, and the method of quitting smoking.
2. Basic requirements
(1) Learning symptoms, diseases and cases:
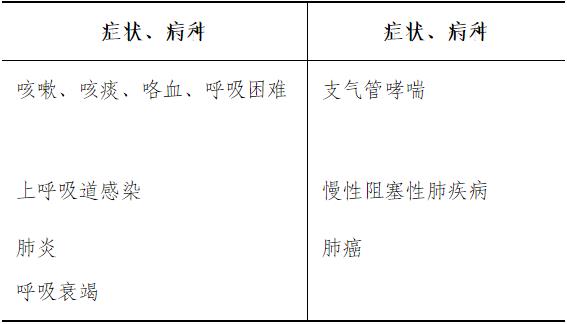
Participate in the management of the number of inpatients is not less than 10 cases.
(2) Basic inspection and operation trainee
Emergency department (1 month)
1. Rotation purpose
Mastery: Basic methods of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR).
Familiarity: clinical characteristics and preliminary treatment of common emergencies; Commonly used first aid drugs (cardiopulmonary resuscitation, anaphylactic shock, etc.).
Understand: emergency department working mode, triage grading standard, emergency department prevention and control workflow and special requirements of prevention and control, including nursing workflow and characteristics.
2. Basic requirements
(1) Learn the disease requirements: common antibiotics for lung infection and treatment of drug-resistant infection, screening and disposal of emergency influenza cases, identification of rash caused by clinical drug allergy, and participation in the treatment of resuscitation cases from cardiac and respiratory arrest.
(2) Clinical first aid skills: master the implementation methods of basic cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
Internal medicine ICU/ respiratory ICU/ comprehensive ICU (for one month)
1. Rotation purpose
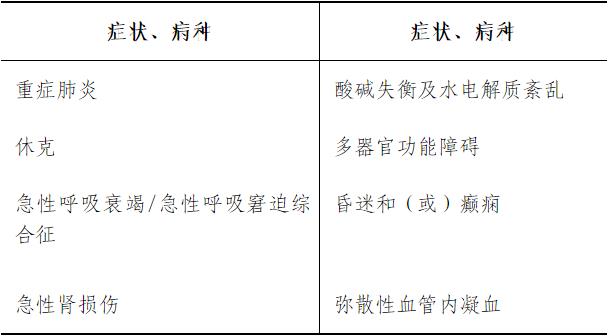
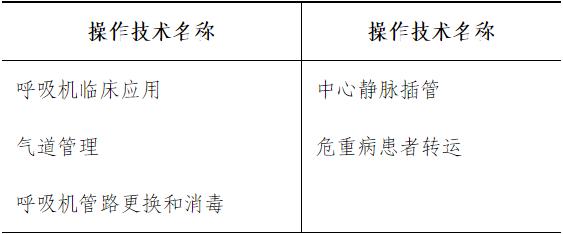
Familiar with: evaluation and transport of critically ill patients; Airway management; Basic hemodynamic monitoring; Clinical application of commonly used first-aid drugs (cardiopulmonary resuscitation and vasoactive drugs, antibacterial drugs, antiarrhythmic drugs, antispasmodic and antiasthmatic drugs, etc.); Diagnosis, treatment and isolation of multidrug-resistant bacterial infections.
Understand: the basic principle and common modes of mechanical ventilation; Deep venous thromboembolism; Severe systemic infection and septic shock; Sedation and analgesia; Monitoring of nervous system function; Indications and clinical application of nutritional support.
2. Basic requirements
(1) trainee symptoms, disease requirements
(2) Basic skills training
Sensory control office (1 month)
1. Rotation purpose
Master:
Laws, regulations, rules and regulations related to hospital infection management, key technologies of hospital infection prevention and control, including methods of hospital infection monitoring, principles of disinfection, standard prevention and isolation, prevention and control requirements of multi-drug resistant bacteria infection, prevention and control requirements of surgical site infection, monitoring and control requirements of central venous catheter-related infection, catheter-related urinary tract infection and ventilator-associated pneumonia, and key requirements of infection prevention and control in key departments such as operating room, disinfection supply center and infectious diseases department. Disease prevention and control hospital management process, medical staff’s own protection knowledge and skills, etc.
The legal and regulatory requirements, systems and processes of disease control, especially infectious disease management, infectious disease reports, management points of fever clinics, and the connection mechanism with hospital infection management and off-campus management departments.
Understand:
Diagnostic criteria of hospital infection cases, common methods and technical points of hospital disinfection, key points of isolation technology and key points and difficulties in implementation. Key points and difficulties in hospital infection prevention and control in key parts and departments. Difficulties in the implementation of disease prevention and control in hospitals.
Occupational protection of medical staff, monitoring of various diseases including respiratory infectious diseases and AFP, health education of patients, management of chronic diseases of patients, management of disease control information, etc.
2. Basic requirements
(1) be familiar with the basic requirements and key points of relevant laws, regulations, systems and processes of hospital infection management.
(2) Complete hospital infection monitoring in 3 internal medicine wards, 3 surgical wards and 1 intensive care unit (completed under the guidance).
(3) Participate in monthly on-site supervision of wards and intensive care units.
(4) Complete the study of infection prevention and control points and supervision points in key departments such as operation department, disinfection supply center, intensive care unit, hemodialysis center and endoscopic center.
(5) to participate in the management and supervision of occupational protection of medical staff in the whole hospital.
(6) Be familiar with the laws, regulations, systems, processes, management principles and requirements of hospital infection prevention and control of infectious diseases.
(7) Master the management requirements and key points of fever clinic.
(8) Grasp the key points and difficulties of infectious disease management, especially respiratory infectious disease management.
3. Higher requirements
(1) Management requirements for the rational use of antibacterial drugs.
(2) Participate in a project of hospital infection prevention and control and implement it.
(3) can independently handle and manage the hospital infection management in the ward.
(4) To design an investigation scheme for the cluster epidemic situation of hospital infection.
(5) Be able to independently inspect the work of infection control and infectious diseases in fever clinics.
(6) Be able to independently coordinate and handle the management requirements and procedures of patients with respiratory infectious diseases in the hospital.
(2) Personnel of pre-hospital medical emergency institutions
Participate in the daily work and teaching activities of the Sense Control Department by participating in patient management, clinical rounds and various teaching activities. Learn professional theoretical knowledge related to the training requirements of the ability of combining medical treatment with prevention.
Infectious Disease
1. Rotation purpose
Familiar with:
(1) Disinfection, isolation and protection measures for infectious diseases;
(2) novel coronavirus’s knowledge of etiology, epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic basis, differential diagnosis and treatment principles;
(3) Etiological knowledge, epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic basis, differential diagnosis and treatment principles of influenza and avian influenza;
(4) Etiological knowledge, epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic basis, differential diagnosis and treatment principles of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome and plague;
(5) Principles of diagnosis, differential diagnosis and treatment of intestinal infectious diseases such as typhoid fever, bacillary dysentery, amoebiasis and bacterial food poisoning; Etiological knowledge, epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic basis, differential diagnosis and treatment principles of norovirus-infected diarrhea;
(6) Etiological knowledge, epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic basis, differential diagnosis and treatment of hepatitis A, B, C and E; Antiviral treatment of chronic hepatitis B and hepatitis C;
(7) Etiological knowledge, natural history, clinical manifestations, primary screening and confirmation, and antiviral treatment principles of human acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS);
(8) Reporting and handling procedures for legal infectious diseases.
Understand:
(1) Clinical epidemiology and prevention of nosocomial infection;
(2) Etiological knowledge, epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic basis, differential diagnosis and treatment of new Bunia virus infection (fever with thrombocytopenia syndrome);
(3) Etiological knowledge, epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic basis, differential diagnosis and treatment of yellow fever, dengue fever, Zika and malaria;
(4) Etiological knowledge, epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic basis, differential diagnosis and treatment of anthrax and brucellosis; Etiological knowledge, epidemiology, clinical manifestations, diagnostic basis, differential diagnosis and treatment of Ebola hemorrhagic fever
(5) Diagnosis and treatment of parasitic diseases;
(6) Pathogenesis and anti-shock treatment of sepsis and septic shock;
(7) Clinical application of antibacterial drugs.
2. Basic requirements
(1) learning symptoms, disease requirements:
No less than 12 inpatients are required to participate in the management.
(2) Basic skill requirements:
Procedures for disinfection and isolation; Graded protection requirements. Carry out intensive practice rotation in fever clinic
3. Higher requirements
On the basis of basic requirements, you should also learn the following diseases and skills.
(1) learning diseases:
Diagnostic thinking of infectious mononucleosis, toxoplasmosis, rabies and fever of unknown origin.
(2) Clinical skill requirements:
Lumbar puncture operation (2 cases on probation).
Emergency department (1 month)
1. Rotation purpose
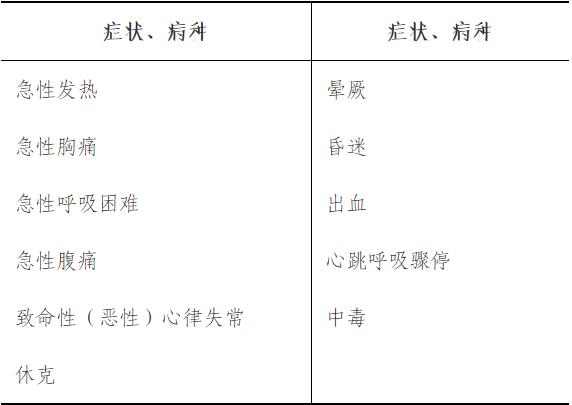
Master: classification standard of patients admitted in hospital, judgment of disease severity, disease severity and risk score, diagnosis and treatment process of chest pain center, and diagnosis and treatment process of stroke center; Master the reporting process and prevention and control points of infectious diseases in emergency; Basic theory and progress of cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR); Diagnostic thinking, differential diagnosis and treatment of common emergencies; Selection, result judgment and clinical significance of auxiliary examination for common emergencies; Rational clinical use of commonly used first-aid drugs (cardiopulmonary resuscitation and vasoactive drugs, cardiotonic diuretics, antispasmodic and antiasthmatic drugs, analgesics, hemostatic drugs, antiarrhythmic drugs, etc.).
Understand: the principles of handling various crises (such as hypertension crisis, thyroid crisis, etc.), serious disorder of water electrolyte and acid-base balance.
2. Basic requirements
(1) learning symptoms, disease requirements:
The total number of patients who are required to participate in the consultation and treatment is not less than 50.
(2) Basic skill requirements:
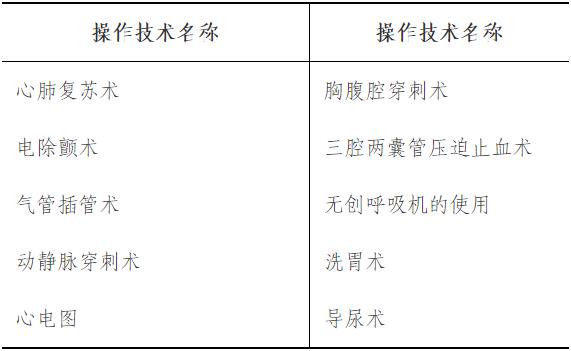
3. Higher requirements
On the basis of basic requirements, you should also learn the following diseases and skills.
(1) disease requirements: multiple organ dysfunction syndrome (MODS)
(2) Clinical knowledge and skill requirements: the basic clinical application of invasive ventilation.
(3) Report 2 clinical cases (PPT presentation)
Respiratory medicine (1 month)
1. Rotation purpose
Master: the diagnostic thinking and differential diagnosis of hemoptysis, chest pain and dyspnea; Pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, differential diagnosis and treatment of common respiratory diseases (pneumonia, bronchial asthma, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, pulmonary embolism, respiratory failure and pneumothorax); Usage and rational application of inhaled drugs; Indications and contraindications of bronchoscopy and medical thoracoscope examination and treatment; Interpretation of arterial blood gas analysis.
Understanding: lung cancer, sleep apnea hypopnea, pleural effusion; Mechanical ventilation and noninvasive ventilation technology; Atomization therapy; Interpretation of lung function examination.
2. Basic requirements
(1) Learning symptoms, diseases and cases:
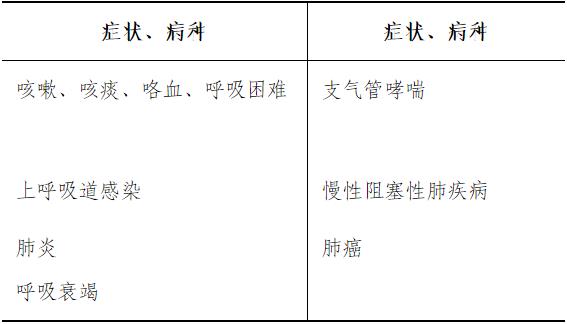
It is required to participate in the management of at least 10 inpatients.
(2) Basic skills training:
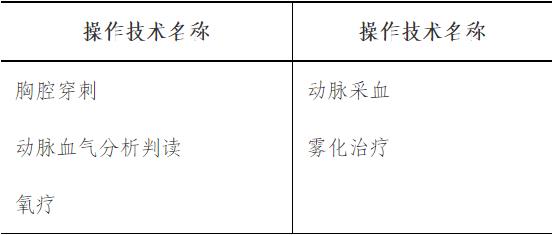
3. Higher requirements
On the basis of basic requirements, you should also learn the following diseases and skills.
(1) learning diseases:
Lung cancer, tuberculosis, pleural effusion, sleep apnea hypopnea syndrome.
(2) Clinical knowledge and skills requirements:
Probation: bronchoscopy, pulmonary function examination, polysomnography and respiratory monitoring. Imaging examination and interpretation of common respiratory diseases;
Participation: mechanical ventilation, noninvasive ventilation.
(3) Requirements for foreign language, teaching, scientific research and other abilities:
Complete a foreign literature review or reading report, and participate in teaching and research activities.
Cardiovascular Department (1 month)
1. Rotation purpose
Master: applied anatomy and physiology of cardiovascular system; Anatomical and functional characteristics of cardiac conduction system; Diagnostic ideas and differential diagnosis of common symptoms of cardiovascular system (including chest pain, dyspnea, palpitation, syncope and dizziness); Pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, differential diagnosis and treatment of common cardiovascular diseases; Diagnosis and treatment of acute and severe cardiovascular diseases; Rational use of commonly used drugs for cardiovascular diseases; Chest x-ray manifestations of common cardiac morphological abnormalities; Common typical ECG diagnosis; Electrical defibrillation technology.
Understanding: Basic knowledge of cardiac electrophysiology, coronary angiography, PCI therapy, pericardiocentesis, cardiac pacing, ambulatory electrocardiogram, ambulatory blood pressure and echocardiography.
2. Basic requirements
(1) Learning symptoms, diseases and cases:

No less than 15 inpatients are required to participate in the management.
(2) Basic skills training:
3. Higher requirements
On the basis of basic requirements, you should also learn the following diseases and skills.
(1) learning diseases:
Pericardial disease, pulmonary vascular disease, infective endocarditis, common adult congenital heart disease.
(2) Clinical knowledge and skills requirements:
Understanding: pericardiocentesis, temporary cardiac pacing.
Interpretation of the report: ambulatory blood pressure, ambulatory electrocardiogram and echocardiography.
(3) Requirements for foreign language, teaching, scientific research and other abilities:
Complete a foreign literature review or reading report, and participate in teaching and research activities.
Internal medicine ICU/ respiratory ICU/ general ICU(1 month)
1. Rotation purpose
Master: diagnosis and emergency treatment of common critical diseases; Evaluation and transport of critically ill patients; Airway management; Basic principles and common modes of mechanical ventilation; Basic hemodynamic monitoring; Clinical application of commonly used first aid drugs (cardiopulmonary resuscitation and vasoactive drugs, antihypertensive drugs, antiarrhythmic drugs, antispasmodic and antiasthmatic drugs, antiepileptic drugs, etc.); Infection and clinical application of antibacterial drugs; Indications of blood transfusion; Indications and clinical application of nutritional support; Diagnosis and treatment of acid-base imbalance and electrolyte disorder.
Understanding: Advanced cardiac life support therapy (ACLS); Tension pneumothorax; Venous thromboembolic diseases; Severe systemic infection and septic shock; Bedside respiratory function monitoring (airway resistance, respiratory system compliance); Bedside cardiac output monitoring (preload, afterload, myocardial contractility); Sedation and analgesia; Monitoring of nervous system function (intracranial pressure, jugular bulb oxygen saturation).
2. Basic requirements
(1) Learning symptoms, diseases and cases:
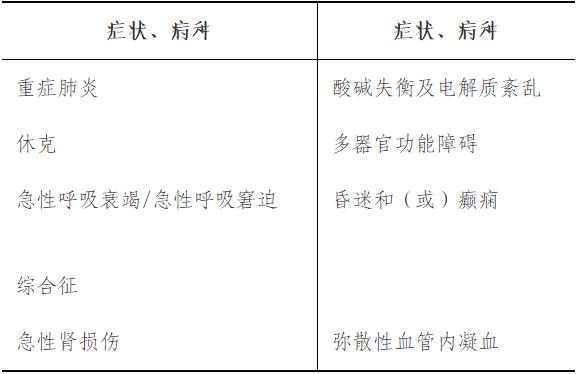
It is required to participate in the management of at least 10 inpatients.
(2) Basic skills training:

3. Higher requirements
On the basis of basic requirements, you should also learn the following diseases and skills.
(1) disease requirements:
Tension pneumothorax, venous thromboembolic diseases, severe systemic infection and septic shock.
(2) Clinical knowledge and skills requirements:
Arterial puncture (operation), bedside cardiac output and respiratory function monitoring, head, chest and abdomen imaging examination and interpretation, nervous system function monitoring, tension pneumothorax diagnosis and treatment.
(3) Requirements for foreign language, teaching, scientific research and other abilities:
1 foreign literature review or reading report; Participate in teaching and scientific research activities.
Sensory control office (1 month)
1. Rotation purpose
Master: requirements, systems and processes of relevant laws and regulations on hospital infection management and infectious disease management, key technologies of hospital infection prevention and control, including methods of hospital infection monitoring, standard prevention, principles of hand hygiene and disinfection, isolation principle, requirements for hospital infection prevention and control of multi-drug resistant bacteria, and disposal of medical wastes. Emergency plan for prevention and control of nosocomial infection, knowledge and skills of medical staff’s own protection, hospital management process of disease prevention and control, and requirements for reporting infectious diseases.
Understand: the commonly used methods and technical points of hospital disinfection, the key points of isolation technology and the key and difficult points of implementation. Difficulties in hospital implementation of disease prevention and control.
2. Basic requirements
(1) through the diagnosis and treatment work, master the hospital infection management and infectious disease management related laws and regulations, systems and processes.
(2) Master the principles and reporting requirements of hospital infection prevention and control of infectious diseases.
(3) Through clinical diagnosis and treatment, master the standard prevention, hand hygiene, prevention and control measures of multi-drug resistant bacteria infection, etc.
(4) Through clinical diagnosis and treatment, master the reporting requirements of pre-inspection and triage and infectious diseases.
(5) Through clinical practice, master the classification requirements of medical staff’s self-protection, the corresponding protection skills and the emergency treatment process of occupational exposure.
(6) Through drills, master the emergency plan and disposal process of hospital infection prevention and control.
3. Higher requirements
(1) through the diagnosis and treatment work, master the hospital infection monitoring methods and diagnostic criteria.
(2) Master the rational use of antibacterial drugs.
(3) Complete the study of infection prevention and control points and supervision points in key departments such as emergency department, ward, operation department, disinfection supply center, intensive care unit, hemodialysis center and endoscopic center.
(4) Understand the requirements and measures of isolation and the classification and disposal of medical wastes.
(5) Be familiar with the specific requirements and measures of infection prevention and control in various invasive operations.
Fourth, training registration
(1) CDC unit: Beijing Center for Disease Control and Prevention.
Tel: 64407255
(2) Pre-hospital medical emergency system Unit: Beijing Emergency Center
Tel: 66098037
Annex 3
Detailed rules for pre-hospital medical first aid ability training
I. Training Time
On-the-job training lasts for 3 months, including 1 week of rotation training, 1 week of internship with the car and 10 weeks of independent duty.
Second, the training place
Beijing Emergency Center and emergency center stations in all districts (excluding Xicheng District)
Third, the training content
(1) Rotation training
Pre-hospital medical emergency work flow, the use of commonly used emergency supplies and equipment, the handling and transshipment of patients, the identification and disposal of common acute and critical patients in pre-hospital medical emergency, the four basic techniques of trauma, the classification and on-site disposal of emergencies, etc.
(2) Internship with the car
One-on-one internship with the car under the guidance of the teaching teacher, familiar with the daily workflow of pre-hospital medical first aid, and master the contents learned in the theoretical training course.
(3) Independent duty service
Independent completion of pre-hospital medical emergency work, in principle, according to the way of 4 shifts and 2 operations, that is, day shift, night shift, night shift and rest, the specific emergency center station is responsible for management.
关于作者