
The Grand Canal is a precious legacy left by our ancestors, bearing the long history and cultural context of the nation. In the new era, the Grand Canal has been endowed with new values and functions to inherit the precious cultural heritage of the Chinese nation and carry forward the excellent traditional Chinese culture. Facing the new requirements of protecting, inheriting and utilizing the Grand Canal, it is urgent to strengthen the management and protection of the river water system, improve the resource conditions of the river water system, improve the function of flood control and drainage, promote the function of water conservancy and water transportation, and support the cultural protection and inheritance and utilization of the Grand Canal.
Characteristics and functions of the Grand Canal water system
The Grand Canal was excavated in the Spring and Autumn Period in the 5th century BC and has a history of more than 2,500 years. During the Sui and Tang Dynasties, the Sui and Tang Grand Canal centered on Luoyang was built on the basis of dredging existing rivers. During the Yuan Dynasty, the skeleton of the Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal was formed by cutting and straightening Tongji Canal and Yongji Canal and digging Huitong River and Tonghui River. During the Ming and Qing Dynasties, the Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal gradually became the main line of north-south water transport. After the founding of New China, the Grand Canal has become the main waterway running through the eastern coastal areas of China, and it is also one of the busiest shipping lanes in the world.
The Grand Canal takes water as its soul and river as its pulse. In the course of more than two thousand years’ development, it has formed the Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal with Beijing as its destination, the Sui and Tang Grand Canal with Luoyang and Kaifeng as its center, and the East Zhejiang Canal. The Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal includes seven sections: Tonghui River, North Canal, South Canal, Huitong River, Middle Canal, Huaiyang Canal and Jiangnan Canal. The Grand Canal in Sui and Tang Dynasties includes Yongji Canal and Tongji Canal.
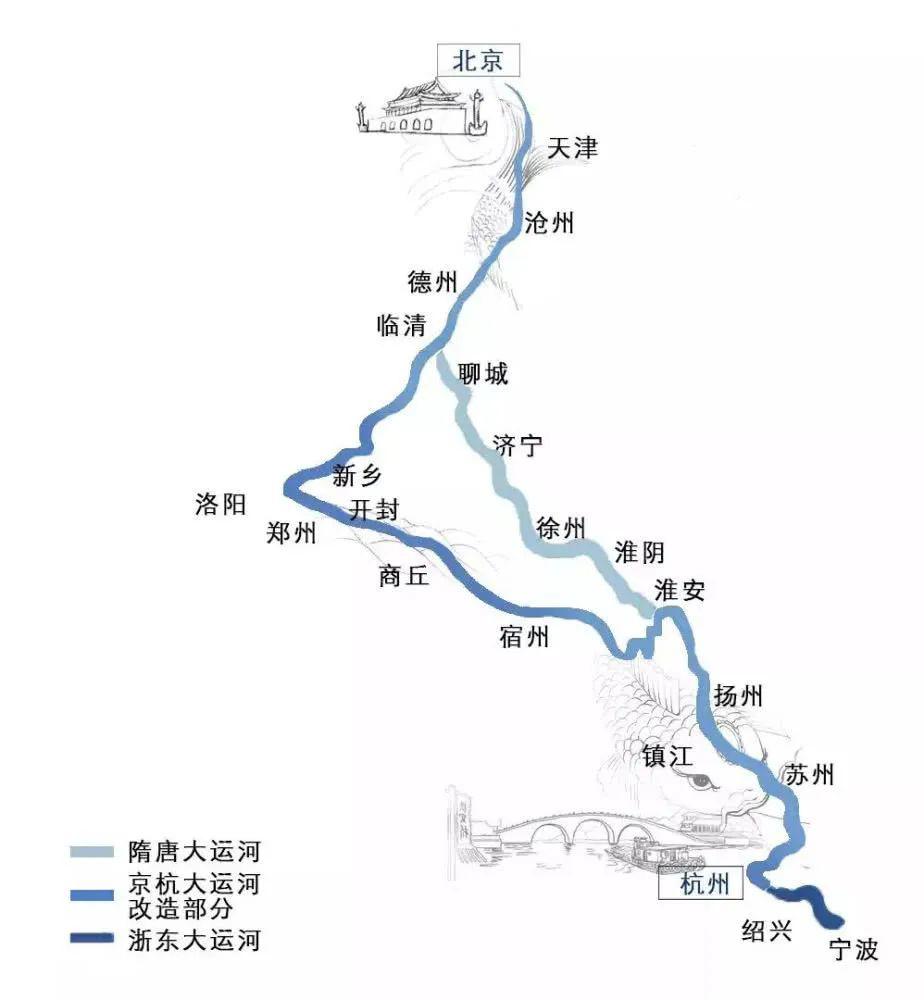
1. Distribution characteristics of water system
(1) the geographical space span is large.
The Grand Canal, with a total length of more than 3,200 km, spans 10 latitudes and 2 climatic zones, runs through the eastern plain of China, and spans eight provinces (municipalities directly under the central government) including Beijing, Tianjin, Shandong, Henan, Anhui, Jiangsu and Zhejiang. The terrain along the route is quite different, and the climate changes obviously. The average annual precipitation for many years ranges from 500mm to 1400mm, making it one of the longest canals spanning latitudes in the world.
(2) communicate with many rivers and lakes.
The Grand Canal runs through the north and south, connecting five natural water systems, namely Haihe River, Yellow River, Huaihe River, Yangtze River and Qiantang River, and connecting lakes such as gaoyou lake, Hongze Lake, luoma lake, Nansi Lake and Dongping Lake in series. Through thousands of years of manual intervention and regulation, it has dug and dredged many natural river sections, connected the original artificial water transport channels of rivers, lakes and depressions, and is an important channel to communicate the water systems in the north and south of China.
(3) Rich cultural heritage resources
The Grand Canal is a great creation in the history of water conservancy projects in the world, which brings together many advanced water conservancy ideas and the essence of hydraulic technology in ancient times. There are more than 1,200 material and cultural heritages along the Grand Canal, including river heritage, hydraulic heritage, affiliated heritage and related heritage. The Grand Canal is the mother river of Cangzhou, Liaocheng, Jining, Xuzhou, Huai ‘an, Yangzhou and other cities along the coast. It forms the regional cultures of Beijing, Tianjin, Yanzhao, Qilu, Zhongyuan, Huaiyang and wuyue, as well as various cultural forms. It embodies the splendid culture of Chinese civilization for thousands of years and is an important carrier for inheriting Chinese history and culture.
(4) Economic status is important
The Grand Canal runs through six provinces and two municipalities directly under the central government in the eastern plain of China, and the areas along it carry more than one-third of the population with less than one-tenth of the country’s land, contributing nearly half of the country’s total economic output. It is one of the regions with the most developed economy and society and the strongest development momentum in China. Despite the alternation of dynasties and historical changes for thousands of years, the position of the Grand Canal as the political, economic and cultural artery of each era has been maintained to this day, and the spirit of the Chinese nation’s pursuit of unity, prosperity and civilization has been organically brought together, which has always been an important link connecting China’s political and economic centers.
2. Function and function
After more than 2,000 years’ development and evolution, the Grand Canal has experienced the military era and the water transportation era. It is not only an important channel for communication between north and south shipping, but also a backbone channel for cross-basin flood and drainage. At the same time, it also undertakes the task of transferring water from South to North. In addition to cultural inheritance, it also plays a variety of functions such as flood control and drainage, water supply and irrigation, inland navigation and ecological landscape.
(1) Flood control and drainage function
The Grand Canal runs through the middle and lower reaches of rivers and plains, and its main function is flood control and drainage. A number of river sections undertake urban flood control and drainage functions, and the southern section of the Yellow River meets the water systems of the plain river network along the way, bearing the flood control and drainage functions of the hinterland of Huaihe River and Taihu Lake basin, which not only ensures the safety of the canal itself, but also ensures the protection tasks of major cities, key areas and cultural heritage along the route.
(2) Water and water supply function
Some sections of the Grand Canal have undertaken the task of water transfer and water delivery in the East Route of South-to-North Water Transfer Project, and played an important role in the construction of China’s water resources allocation pattern of "four horizontals and three verticals, north-south allocation and mutual aid between east and west". In the 1156km water delivery line of the East Route of South-to-North Water Transfer Project, 750km of the Grand Canal is used, and the second phase is also planned to use some rivers such as the South Canal to deliver water. In addition, some sections of the Grand Canal also undertake regional water transfer or emergency water transfer tasks, such as water diversion from Jiangsu Province to the North, water diversion from eastern Zhejiang, and water diversion from the Yellow River to Tianjin.
(3) inland navigation function
Water transport is one of the important functions of the Grand Canal. The Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal, south of Dongping Lake in Shandong Province, has a navigable reach of 1050km, which is the "golden waterway" next to the Yangtze River in China. South of the Yellow River, except the Zhejiang section of the Jiangnan Canal and the East Zhejiang Canal, the other sections are Class II ~ III waterways. Since 1970s, the navigation in the north of the Yellow River has been gradually cut off. Only some sections of the Yellow River are reserved for tourist navigation, and the sections from Beiguan Gate of the North Canal to Gan Tang Rubber Dam and Tianjin are seasonal tourist navigation.
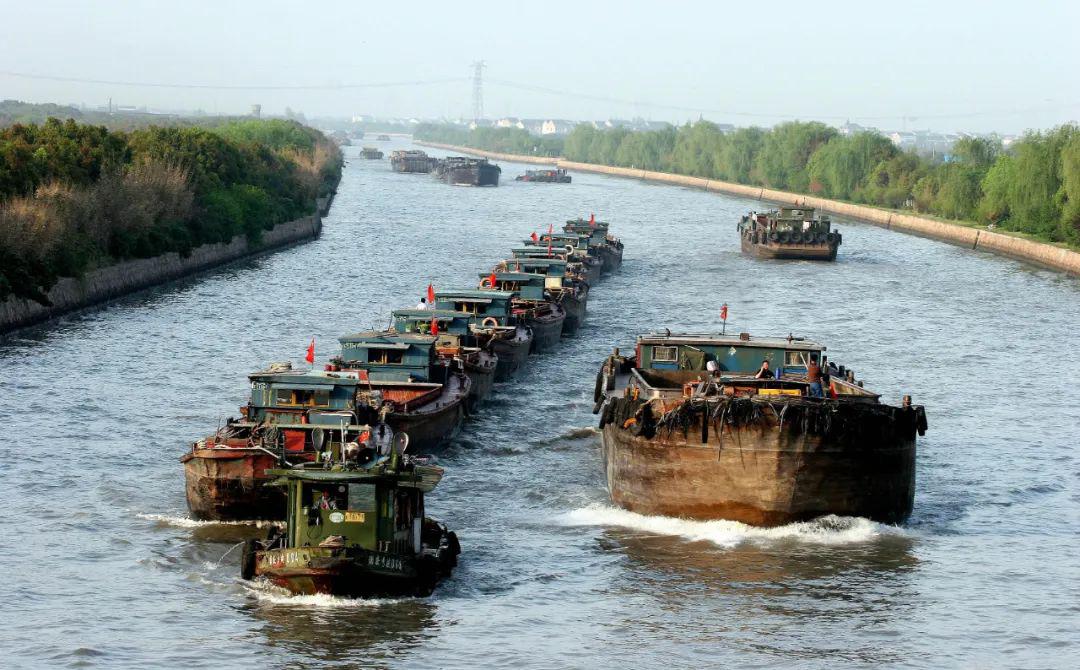

▲ The Grand Canal carries important water transport functions.
(4) Ecological landscape function
The long history of water transportation in the Grand Canal has formed a cultural belt with the Grand Canal as the core. For example, the pattern of Beijing urban water system was formed on the basis of the opening of Tonghui River in Guo Shoujing in the Yuan Dynasty. Suzhou, Yangzhou, Jiangsu, Hangzhou, Shaoxing, Zhejiang, etc. are all typical city representatives who rely on the Grand Canal to become rich in the charm of Jiangnan water towns. With the Grand Canal becoming a world cultural heritage, Tongzhou Grand Canal Forest Park, North Canal Country Park, Jiangdu Water Conservancy Project, Shaobo Lake and other cultural sites publicity exhibition halls have been built one after another, and the ecological and cultural functions of the Grand Canal have become increasingly prominent.
Present situation of management and protection of grand canal
The General Secretary of the Supreme Leader pointed out that the Grand Canal is a precious legacy left by our ancestors and a flowing culture, which should be well protected, passed down and utilized, pointing out the direction for the management and protection of the Grand Canal. In February, 2019, the Outline of the Planning for Cultural Protection, Inheritance and Utilization of the Grand Canal (hereinafter referred to as the Outline) issued by the Central Office and the State Council called for the construction of the Grand Canal cultural belt as the core, the creation of splendid cultural belts, green ecological belts and colorful tourist belts, and the continuation of the Millennium charm of the magnificent canal, making it a beautiful business card to promote China’s image, show Chinese civilization and show cultural self-confidence in the new era, and put forward the functional orientation around different sections of the Grand Canal, making overall plans. In December 2019, the Central Office and the State Council issued the "Construction Plan for the Great Wall, the Grand Canal and the Long March National Cultural Park", and the Grand Canal entered the ranks of key national cultural parks, which put forward specific requirements for building national cultural parks, making the Grand Canal an important symbol of Chinese culture, and carrying out river water system management and management. In recent years, provinces, cities and relevant state departments along the route have carried out a lot of work around the protection and utilization of the Grand Canal, and achieved remarkable results. However, in the face of the new situation and new requirements of protecting, inheriting and utilizing the Grand Canal, the management and protection of the river system of the Grand Canal is still insufficient.
First, there is a serious shortage of water resources in the northern section of the Yellow River, resulting in the disconnection of some sections.North China, where the northern section of the Yellow River of the Grand Canal is located, is one of the regions with the most scarce water resources in China. With the rapid economic and social development and the continuous improvement of urbanization level, the regional water consumption is gradually increasing, and the development and utilization of water resources are seriously overloaded, resulting in serious over-exploitation of groundwater in North China, forming a number of groundwater level drop funnels. The rivers such as the North Canal and the South Canal have been cut off for a long time, and the Weihe River and the Wei Canal have been cut off seasonally or even dried up for a long time. Even after the first phase of the South-to-North Water Transfer Project is opened, it still cannot
Second, the flood control and drainage system is not perfect, and there are outstanding weak links.The Haihe River, Yellow River, Huaihe River and Taihu Lake basins through which the Grand Canal passes are frequent and complicated areas in China. In order to eradicate the floods, the state has continuously strengthened the flood control and drainage management in the basins, and most of the river sections have reached the planned flood control and drainage standards, but there are still outstanding weak links, and problems such as river siltation, substandard dikes and insufficient flood discharge capacity are common in the northern section of the Yellow River. Along the Yellow River to the Yangtze River, the terrain is low, the drainage conditions are poor, and the regional flood control and drainage capacity is insufficient; Due to the great encirclement of cities along the Yangtze River and the changes in the construction conditions of polder areas, a large amount of flood water was discharged into the canal in flood season, which led to the high water level of the canal. It is urgent to expand the drainage road of flood water outside the canal to alleviate the flood control pressure of the canal.
Third, the lack of water shoreline protection affects the function of the canal.In order to strengthen the management and protection of rivers and lakes, the Ministry of Water Resources has uniformly deployed and launched a special campaign to clean up the "four chaos" in rivers and lakes across the country. Provinces and cities along the Grand Canal have concentrated on cleaning up and rectifying the "four chaos" in the canals under their jurisdiction, and the appearance of the canals has been significantly improved. With the acceleration of urbanization along the Grand Canal, some river sections have problems of disorderly shoreline development and encroachment on rivers and lakes. Illegal sand mining occurs from time to time in some river sections, which affects the functions of flood discharge, water conveyance and navigation, and poses a certain threat to the protection of the cultural heritage of the Grand Canal.
Fourth, the water pollution load is heavy, and the pressure of water resources protection is great.In recent years, various provinces and cities along the Grand Canal have continuously strengthened water resources protection and water ecological environment management, and achieved good results. However, some sections of the Grand Canal north of the Yellow River were once used as sewage channels, and some sections of the villages and towns were occupied by garbage, which greatly reduced the water environmental capacity. There are many lakes along the reach from the Yellow River to the Yangtze River, and the water body is eutrophic in different degrees because of the purse seine in Nansi Lake and the cultivation along the lake bank. Factories and enterprises on both sides of the south section of the Yangtze River gather, and some enterprises discharge sewage into the river, resulting in a large amount of pollution.
Fifth, the shipping system is not perfect, and the level of green development needs to be improved.The navigation level of the south section of the Grand Canal has been continuously improved, and the freight scale has increased rapidly, which has played an important role in improving China’s comprehensive transportation system and giving play to the advantages of inland waterway economy and environmental protection. However, there are some problems such as substandard navigation channels, insufficient navigation clearance of some bridges, saturated capacity of some shiplocks, and low degree of specialization and intensification of ports. Most sections of the Yellow River north are currently in a state of suspension, and the shipping efficiency and service level need to be further improved.
Sixth, the responsibility of management and protection is not clear, and the management coordination mechanism needs to be improved.Except for some provincial river sections which are directly managed by river basin agencies, the Grand Canal is managed in a territorial way, and a management system involving water conservancy, transportation, cultural relics, tourism and other departments has been established. Due to trans-regional and inter-departmental problems, such as regional division and overlapping responsibilities of departments, it is urgent to establish a coordination mechanism at the national level to coordinate the functions of flood control, water supply, heritage protection, navigation and ecology of the Grand Canal.

▲ Yangzhou section of Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal
Thoughts on management and protection of grand canal
In accordance with the instructions of the Supreme Leader General Secretary on protecting, inheriting and making good use of the Grand Canal and the overall deployment of the construction of the National Cultural Park, and following the water control idea of "giving priority to water conservation, balancing space, systematically managing and exerting efforts with both hands", the general tone of water conservancy reform and development of "making up the shortcomings of water conservancy projects and strengthening supervision of water conservancy industry" is implemented, guided by the functional orientation of different river sections. The main tasks are to improve the water resources conditions of river courses, improve the flood control and drainage guarantee function, promote the shoreline protection and service upgrading, and strengthen the management and protection of the Grand Canal. We will restore and enhance the functions of flood control and drainage, water supply and water supply, inland navigation, ecological landscape and cultural heritage of the Grand Canal, and turn the Millennium Canal into a "flowing river, a safe river, a beautiful river and a wise river" to benefit the people.
The management and protection of the river system of the Grand Canal need to be combined with the new situation and challenges, based on the height of protecting, inheriting and making good use of the Grand Canal, in accordance with the concept of ecological civilization, adhere to the harmonious and green development of people and water, adhere to the priority of water conservation, measure water, adhere to local conditions, implement policies in sections, adhere to overall consideration and comprehensive balance, adhere to reform, innovation, coordination and linkage, and coordinate the following relations.
1. Handle the relationship between protection, inheritance and utilization.
The management and protection of the river system should adhere to the principle of joint protection rather than large-scale development. It is necessary to protect the Grand Canal, its facilities and water cultural heritage, carry forward and inherit its comprehensive functions, and at the same time improve the utilization level of the river system of the Grand Canal.
2. Handle the relationship between needs and possibilities.
We should not only consider the demand for water resources for the construction of green ecological corridors and the realization of tourism navigation in suitable reaches, but also fully consider the water resources conditions and the feasibility of coordinating regional water resources allocation; It is necessary to improve the safety standard of flood control and waterlogging elimination, but also to respect nature and arrange the flood outlet reasonably; It is necessary to promote the protection, restoration and management of water ecological environment in an orderly manner, and strengthen the control of river water coastline.
3. Handle the relationship of "four waters" overall management.
To strengthen the rigid constraint of water resources’ water environment carrying capacity, we should not only consider the relationship between water saving, water distribution, water transfer, water ecological environment improvement and navigation function improvement, but also consider the relationship between water environment management and protection and clean water supply, and also handle the relationship between flood control and drainage and water resources allocation, water resources and water ecological protection.
4. Handle the relationship between governance and control.
Governance and management are two important means to do a good job in the Grand Canal water article, and also reflect the requirements of the general tone of "water conservancy projects make up the shortcomings and the water conservancy industry is strongly supervised". Both governance and management should be paid equal attention to, so as to ensure the reliable function of the Grand Canal and realize the long-term operation of the Grand Canal through management and control.
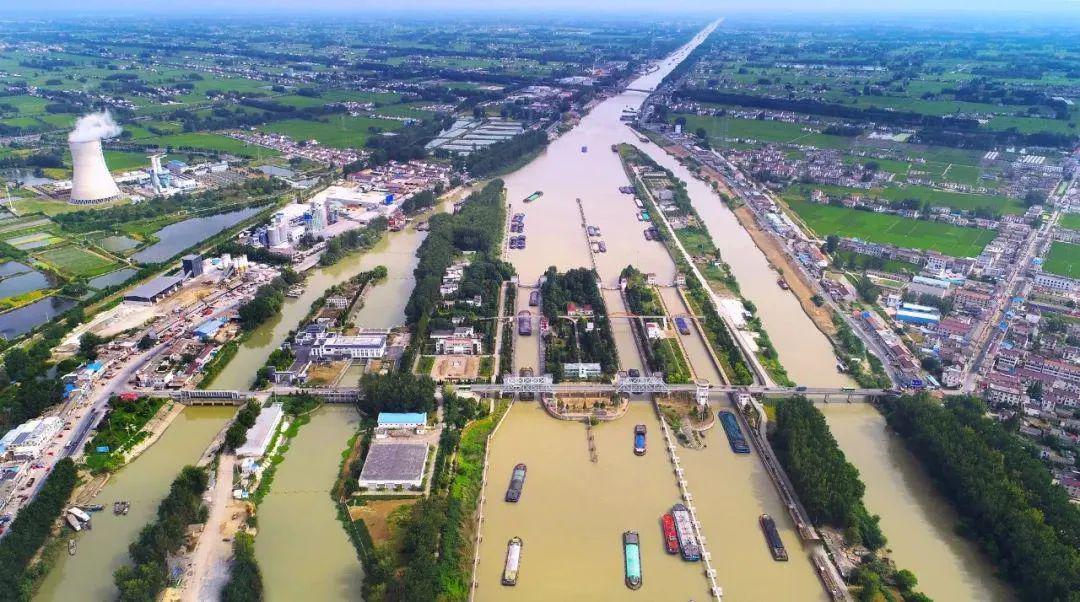

▲ Huai ‘an Ship Lock of Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal
Key points of management and protection of the Grand Canal and countermeasures and suggestions
1. Key points of management and protection
① Improve the resource conditions of river system and build the Grand Canal into a "flowing river". Facing the shortage of water resources in the area north of the Yellow River, in view of the water resources conditions and water demand in different sections of the Grand Canal, we should closely link up the major national strategic requirements such as coordinated development of Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei, construction of xiong’an new area, ecological protection and high-quality development in the Yellow River basin, implement water demand and quantity, take water resources as the greatest rigid constraint, strengthen the economical and intensive utilization of water resources along the Grand Canal, strengthen the control of total water intake, and accelerate the comprehensive management of groundwater overexploitation along the line. Give priority to local water resources, reclaimed water in cities and towns, and properly supplement the water diversion projects such as the South-to-North Water Diversion Project and the Yellow River Diversion Project, optimize the allocation of water resources, actively promote the construction of the second phase of the East Route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project, and strive to achieve water supply throughout the Grand Canal in normal years.
② Improve the function of flood control and drainage, and build the Grand Canal into a "safe long river". In order to ensure the flood control safety of the Grand Canal, it is necessary to focus on ensuring the safety of the Grand Canal and the towns and key cultural heritage sites along it, rely on the flood control and disaster reduction system in the basin and region where the Grand Canal is located, and focus on the river regulation of the Grand Canal, and coordinate the relationship between flood control and water delivery, shipping, river regulation and cultural heritage protection. By optimizing the flood control and drainage layout, improving the flood control and drainage engineering system and strengthening flood risk management, the Grand Canal and its rivers with hydraulic connections can be comprehensively regulated to improve their flood control and disaster reduction capabilities.
③ Strengthen the protection and restoration of water ecology and build the Grand Canal into a "beautiful long river". In order to protect the water ecological environment of the Grand Canal, it is necessary to strengthen the water source protection of the water conveyance channel of the South-to-North Water Transfer Project, ensure the ecological water demand of rivers and lakes, and protect and restore the ecological environment of the Grand Canal, protect and restore the basic forms of the rivers and lakes of the Grand Canal, restore the green vitality of the Grand Canal, enhance the water ecological service function of the Grand Canal, and build a green ecological corridor running through the north and south.
④ Promote shoreline protection and service improvement, and build the Grand Canal into an "ecological river". To manage the "basin filled with water" of the Grand Canal, it is necessary to strictly control the waterfront space of the Grand Canal, clarify the functional zoning and control requirements of the coastline, standardize the development and utilization of the canal coastline, strictly manage sand mining, promote the construction of water conservancy infrastructure network, strengthen the maintenance of water conservancy projects, strengthen the protection and utilization of water conservancy heritage, and strive to restore the clean and tidy appearance of the river, so as to make revetment an important part of the cultural ecosystem of the Grand Canal.
⑤ Improve shipping efficiency and service level, and promote the green development of shipping. In order to further promote the green development of the Grand Canal shipping, it is necessary to steadily promote the navigation in the appropriate section of the Beijing-Hangzhou Grand Canal north of the Yellow River, upgrade the shipping in the southern section of the Yellow River and the eastern Zhejiang Canal, and promote the tourism navigation in the appropriate section of the Sui and Tang Dynasties Grand Canal, and comprehensively improve the shipping efficiency and service level by means of reaching the standard, upgrading the port and developing green ships.
⑥ Innovate the water management system and mechanism to build the Grand Canal into a "long river of wisdom". In order to further improve the coordinated linkage mechanism of river system management and protection of the Grand Canal, it is necessary to speed up the construction of a coordinated linkage, intelligent management and control, monitoring and early warning, and emergency response mechanism for the Grand Canal river system, relying on the system of river length and lake length, taking the implementation of the most stringent water resources management system as the starting point, taking the intelligent management and protection of river system as the means and strengthening the prevention and control of water safety risks as the bottom line.
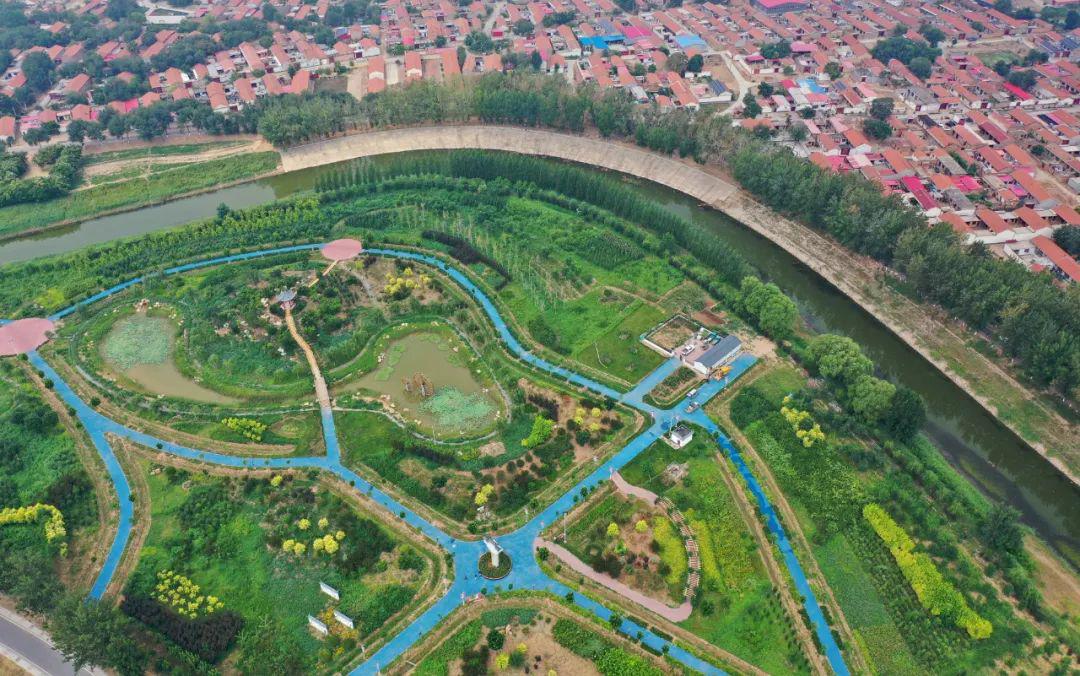

▲ The barren beach of the Grand Canal in Qingxian County, Hebei Province turned into an ecological park
2. Policy recommendations
(1) Accelerate the construction of the follow-up project of South-to-North Water Transfer Project.
Shandong and Henan provinces have all allocated and licensed water use indicators for the Yellow River, and only relying on local water, the northern section of the Grand Canal will be difficult to meet the objectives of water supply and water ecological protection and restoration proposed in the Outline, and must rely on external water transfer. It is suggested that, on the basis of giving full play to the water supply capacity of the first phase of the East Route of South-to-North Water Transfer Project, the emergency water supply project of the first phase of the East Route should be accelerated, and the river diversion, yellow river diversion and local water resources should be rationally dispatched to speed up the construction of the second phase of the East Route of South-to-North Water Transfer Project.
(2) further implement the system of river length and lake length.
Promote the length of rivers and lakes at all levels from "famous" to "real", clarify the length and responsibilities of rivers and lakes along the Grand Canal, and supervise the implementation of the river length system and the performance of the river length. Formulate the "one river, one policy" management plan and action plan for the Grand Canal, define the tasks in water resources protection, water shoreline management and protection, water pollution prevention and control, water environment management, water ecological restoration, law enforcement and supervision, and put forward detailed implementation plans and management and protection measures. Establish the responsibility system of lake length with the responsibility system of provincial and municipal party and government leaders as the core, implement the management and protection personnel, funds and assessment mechanism, build a long-term mechanism for lake management and protection, and establish an inter-administrative coordination mechanism for lake length.
(3) to speed up the construction of water laws, regulations, policies and systems of the Grand Canal.
To speed up the construction of water laws and regulations of the Grand Canal, it is suggested that the documents of water conservancy laws and regulations of the Grand Canal should be formulated, and the provincial and municipal governments along the route should improve the local laws and regulations on the protection and management of the Grand Canal, so as to realize the institutionalization, standardization and proceduralization of water management of the Grand Canal. Establish a unified law enforcement agency for the Grand Canal, learn from the management experience of Suez Canal, Panama Canal and Midi Canal in France, coordinate the water law enforcement forces along the Grand Canal, focus on illegal sewage discharge along the coast, shoreline occupation, "black wharf" and illegal sand mining, and organize joint law enforcement activities across provinces, cities and departments to maintain the trend of cracking down on illegal activities along the Grand Canal. Strengthen the guidance and inspection of the administrative law enforcement work of the provincial and municipal authorities along the line, and establish a supervision and notification system for water disputes and illegal wading cases.
(4) Create a "wisdom canal" with the help of new technologies.
Make full use of new technologies such as Internet of Things, cloud computing and big data, build a unified monitoring network platform along the Grand Canal, build big data at all levels, professions and related industries, and build a large system of business support, decision support and public service support, build a "smart canal", strengthen perception, expand network coverage and support capabilities, promote information sharing, and continuously improve the scientific decision-making level of water management in the Grand Canal.
Published in China Water Conservancy, No.22, 2020, with the original title "Ideas and Countermeasures for River System Management and Protection of Grand Canal".
Author/Yuan Lee Garden (Vice President and Professor-level Senior Engineer, General Institute of Water Resources and Hydropower Planning and Design, Ministry of Water Resources), Huang Huojian, Yang Xiaoru, Zhang Yiqing, Xing Ziqiang and Jiang Dachuan.
关于作者